Executive Summary
The pressing need to curb healthcare spending and use healthcare resources wisely, along with the efficiencies that cloud-based systems offer, are converging factors that make cloud system adoption an advantageous opportunity for healthcare organizations (HCOs) and their laboratories.
This white paper discusses three main advantages that a cloud-based solution offers specific to healthcare information systems:
- Cloud-based systems can increase the security of protected health information. Offloading the bulk of security measures to a cloud vendor makes data more secure and reduces the burden on the organization’s IT staff.
- HCOs that use a cloud-based information system can obtain a cost-effective IT solution without the capital layout or expenditure for internal IT staff to maintain and service the infrastructure. A subscription service levels the cost curve and eliminates costs peaks that occur across time.
- Cloud systems increase data redundancy and system availability (or uptime) by automating backups and disaster recovery options. This added data protection means that an HCO does not lose vital patient data and can minimize downtime.
 For the laboratory, cloud-based solutions can be a highly effective method for expertly managing data, resources, and workflows in a cost-effective, secure manner that reduces the need for IT staff with lab expertise. Orchard Cloud Services offers a secure, reliable, and cost-effective hosting environment for laboratory information systems, where clients are hosted in fully redundant, HIPAA-compliant data centers that protect and secure critical applications. Orchard hosting ensures that information systems are always accessible, allowing our laboratory customers to focus on providing high quality patient care.
For the laboratory, cloud-based solutions can be a highly effective method for expertly managing data, resources, and workflows in a cost-effective, secure manner that reduces the need for IT staff with lab expertise. Orchard Cloud Services offers a secure, reliable, and cost-effective hosting environment for laboratory information systems, where clients are hosted in fully redundant, HIPAA-compliant data centers that protect and secure critical applications. Orchard hosting ensures that information systems are always accessible, allowing our laboratory customers to focus on providing high quality patient care.
Introduction
Greater patient expectations, new payment models, and the growing need to curb healthcare spending, alongside the numerous advantages that cloud hosting offers, make cloud-based systems a beneficial opportunity for healthcare organizations (HCOs) and their labs. As security concerns are addressed and benefits are realized, the global market for healthcare cloud computing is rising rapidly, expected to surpass $55 billion by 2025 (an approximate $48 billion increase from 2018).1
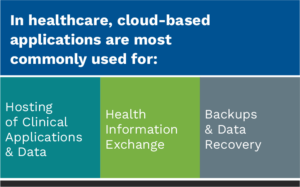
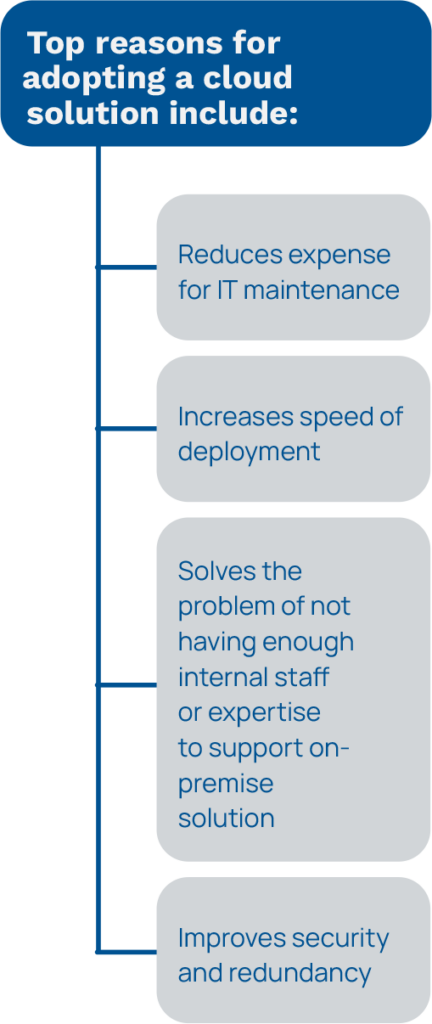
Clinical information systems account for the bulk of the global healthcare cloud-based market share. Adoption of cloud systems for clinical areas can be attributed to a combination of federal incentives, growing image generation, and the need for scalability and sharing patient data.3 Figure 1 lists the most common uses for cloud-based applications specific to healthcare, and Figure 2 lists common reasons for adopting a cloud-based solution. Across the board, the cloud’s advantages are becoming harder to ignore.
“Cloud” Defined
The term “cloud” generically refers to Internet-based computing that shares resources and provides data to connected devices. Users have shared access to applications, servers, and services via the Internet, making data sharing and collaboration easier. National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) categorizes the cloud market into three fundamental service models:
- Software as a Service (SaaS)
- Platform as a Service (PaaS)
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
 |
Software as a Service (SaaS)In SaaS, the applications are hosted by a cloud service provider and made available to users over the Internet. The end user does not control or maintain the underlying infrastructure. SaaS is the largest segment of healthcare cloud computing, likely because SaaS models have been in the market much longer than the other models. |
 |
Platform as a Service (PaaS)With PaaS, application development resources (e.g., hardware, operating systems, programming languages, toolkits) are hosted in the cloud. The user has control over the deployed applications and can develop higher level applications that are hosted on the platform to serve its end users. |
 |
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)The IaaS model provides storage, networks, and computing resources to allow the user to run and execute an operating system, applications, or software of their choice. The user has control over the operating system, applications, storage, and networking components, but does not manage or control the cloud infrastructure. Users typically pay on a per-use basis.
|
Benefits of Cloud Services in Healthcare
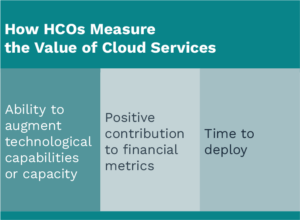
The main advantage of a cloud-based model is that it provides access to massive computing resources that are available on demand that would otherwise not be affordable. Specific to healthcare, cloud systems can increase security of protected health information (PHI), support tools like artificial intelligence and machine learning, and improve the ability for providers and organizations to collaborate and share data. Figure 3 lists the most common ways that healthcare organizations measure the effectiveness of a cloud solution in a healthcare setting.
Cost Efficiency Gains
Costs of an on-premise solution versus a cloud-based solution are not directly comparable because the level of service that a cloud provider can achieve is typically much higher than the service level maintained at an individual organization. This illustrates how one of the main advantages of cloud computing in healthcare is its cost efficiency.
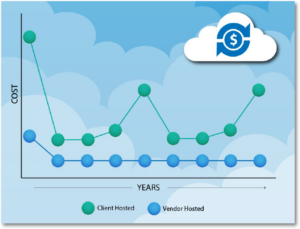
Today’s HCOs spend approximately 75% of their IT budgets to maintain existing on-premise systems.4 Cloud computing reduces the hefty capital expenditure (CAPEX) and levels the cost curve, eliminating cost peaks that occur across time (see Figure 4). Rather than having an initial large expenditure for hardware that must be updated or replaced every three to five years, with the cloud, an HCO pays for a subscription service that becomes an operating expense (OPEX) based on their scale.
This allows organizations to use the money that would have been required to build a robust IT infrastructure in other operational areas. In effect, HCOs that use a cloud-based solution can obtain a cost-effective IT solution without the capital layout or expenditure for internal IT staff to maintain and service the infrastructure.
Hosting on-premise data centers includes ongoing costs of maintaining the servers, physical spaces, cooling solutions, security, etc. Cloud systems can reduce spending for hardware, software, human resources, and IT management. All these resources are less expensive when implemented and managed on a large scale by the cloud vendor. Reducing IT overhead can result in significant savings, and data storage costs are reduced when data can be safely stored without the cost of physical servers.
With an on-premise solution, when 75% of budget dollars are spent just to maintain the infrastructure, there is not much left in the budget for new IT technologies or innovation. With cloud-based solutions, HCOs have access to the latest technologies within a reasonable budget. For many healthcare facilities, access to the most up-to-date technologies can be a competitive edge that makes a difference in their bottom line.
Effective, Affordable Data Security
Furthermore, when clarifying budget restraints, many HCOs get by with low quality or older hardware trying to make dollars go further, making them vulnerable to security threats. This is a serious problem because HCOs are dealing with sensitive patient data that requires enhanced security measures to meet compliance standards and protect patient information.
By offloading the bulk of security measures to the cloud vendor, data becomes more secure, and there is less burden on the organization’s IT staff. As ransomware attacks escalate in frequency and cleverness, it becomes increasingly difficult to stay up to date on the latest phishing and ransomware attacks. The cloud vender can handle these security concerns more easily, as security is a number one priority for all its customers.
While security is one of the biggest benefits of cloud services, it is also one of the most common concerns that executives have when considering moving their sensitive patient data and applications to a data center that is not within their direct control.
Generally, this is a misunderstanding about how cloud security works. As one example, a healthcare worker could physically lose a laptop that has PHI. This scenario is a potential breach that could result in heavy fines for the organization. However, if the HCO is utilizing cloud services, the computer can be remotely wiped, eliminating any opportunity for the data to be inappropriately accessed.
 In addition, in an on-premise solution, when equipment fails, an HCO can possibly lose data and applications—again, a potential breach that is a big risk for a healthcare entity. Cloud computing allows users to access the information remotely and includes automated backups and disaster recovery. In the case of a breach, no data is lost, and downtime is minimized. Cloud providers offer security, risk management, and monitoring services that protect its users from unauthorized access and breaches; they can basically amortize the cost of that security across many servers instead of only a few. There are no on-site servers to wipe out or seriously compromise in the case of natural disasters or malicious cyberattacks.
In addition, in an on-premise solution, when equipment fails, an HCO can possibly lose data and applications—again, a potential breach that is a big risk for a healthcare entity. Cloud computing allows users to access the information remotely and includes automated backups and disaster recovery. In the case of a breach, no data is lost, and downtime is minimized. Cloud providers offer security, risk management, and monitoring services that protect its users from unauthorized access and breaches; they can basically amortize the cost of that security across many servers instead of only a few. There are no on-site servers to wipe out or seriously compromise in the case of natural disasters or malicious cyberattacks.
Business Continuity: Scalability, Flexibility, & Reliability
Although security is one of the cloud’s best features, another tremendous benefit of a cloud solution is its support of overall business continuity—through its ability to improve scalability, flexibility, and reliability. In a healthcare setting, it is critical to have continual access to systems and data, so it becomes of utmost importance to have high availability, including a failover plan in case of an unexpected instance or disaster. To maintain high availability, an HCO must have a recovery strategy and server failover options. Disaster recovery plans must be thoroughly planned out, tested, and documented to ensure reliable access to systems.
In the past, in the event of a system failure, businesses had to either have backup hardware or wait for new equipment to be shipped. It is not entirely feasible for many HCOs to have a full secondary infrastructure to switch to in case of a failure of the primary. Organizations must weigh the cost versus benefit of system availability strategies versus downtime impact.
 Without a doubt, cloud services provide better alternatives for failover options. Most cloud providers replicate data in multiple locations called data centers. In the event of a failure, cloud-hosted solutions enable near seamless transfer from one data center to a backup parallel data center. Cloud systems increase the reliability of data redundancy and system uptime by automating backups and disaster recovery options. Thus, an HCO will not lose data and can minimize downtime. In a natural disaster or technology failure, a cloud provider has multiple options to maintain a system with virtually no downtime. With the cloud, IT departments can maintain almost seamless continuity in service provision. In addition, cloud failover is more cost-effective because the shared resources provide the economy of scale to make pricing of a robust security system affordable. Also, the fact that cloud resources are externally managed reduces maintenance overhead.
Without a doubt, cloud services provide better alternatives for failover options. Most cloud providers replicate data in multiple locations called data centers. In the event of a failure, cloud-hosted solutions enable near seamless transfer from one data center to a backup parallel data center. Cloud systems increase the reliability of data redundancy and system uptime by automating backups and disaster recovery options. Thus, an HCO will not lose data and can minimize downtime. In a natural disaster or technology failure, a cloud provider has multiple options to maintain a system with virtually no downtime. With the cloud, IT departments can maintain almost seamless continuity in service provision. In addition, cloud failover is more cost-effective because the shared resources provide the economy of scale to make pricing of a robust security system affordable. Also, the fact that cloud resources are externally managed reduces maintenance overhead.
Along with that, a cloud provider’s ability to dynamically scale defensive resources on demand has obvious advantages for resilience. Furthermore, cloud computing has rewards related to “green computing.” Green computing means consideration of environmental factors and using computer resources efficiently so that energy is conserved. Usage of ready-made computing resources, such as those found in a cloud-provider facility, helps reduce electricity expenses needed to cool off computers and equipment.5
One consistent aspect of our healthcare environment is that it is always changing. Cloud-based services give HCOs the power to keep up with changes and fluctuating demands without big cost peaks. When a change takes place, the flexibility of the cloud solution allows an HCO to easily scale services up or down to meet current needs. The ability to ramp services up or down is important for businesses that are cyclical or seasonal and those that are growing quickly.
Concerns & Challenges to Consider with Cloud Services
Security and privacy are two of the primary concerns HCOs face when selecting a cloud solution because of the inherent unique privacy and security considerations of patient data. The mere concept of HCOs trusting their sensitive patient data in a public cloud seems at odds with the advanced level of security and industry compliance that is required. The feeling of having less control, along with HIPAA compliance requirements, makes some healthcare leaders hesitant to switch to a cloud-based solution.
When choosing a cloud provider, customers should not treat the cloud solution as a black box, but rather as a partnership where the customer completely understands the cloud’s impact on their patient data. Healthcare Information Technology (HIT) consumers should learn how the cloud solution provides security and meets regulatory requirements, as well as how they can supplement, monitor, and measure security on their end. Cloud customers should ensure that they retain their data and that the cloud provider does not use their data for its own purposes. In order to overcome these concerns, healthcare businesses must choose a reliable cloud provider that incorporates HIPAA compliance in its business model.
Today’s HIT experts agree that moving healthcare services to a cloud provider increases security. As the healthcare cloud market continues to mature, healthcare leadership is shifting its stance of skepticism to one of acceptance of the cloud as a viable (and even better) IT service delivery model. The reality is that properly managed cloud-based solutions strengthen an HCO’s overall cybersecurity structure with additional layers of security and monitoring. The cloud provider has a sincere interest and focus on security, while an on-premise IT team has a multitude of responsibilities. In addition, cloud solutions have large infrastructures that must proactively stay up to date on the latest patches and security measures and likely have access to patches/updates before they are released to the public.6
Cloud vendors have security as a number one priority with 24/7 monitoring by highly trained security staff, whereas a local HIT team may not have the resources or training to monitor security at this level.

Cloud-based Laboratory Information Systems
Historically, laboratory software had to be on a computer or server that could only be accessed at a specific location with physically connected analyzers. Today, that need for physical connectivity has been eliminated. Rather than storing data on local servers, data can be stored remotely and backed up to the cloud, and users can access their data using the Internet.
 Many of Orchard’s LIS customers have reported concerns about the burden of managing their IT infrastructure, monitoring databases for optimal performance, preparing for environmental challenges and unexpected natural disasters, and developing security measures for ransomware attacks and other increased and evolving malicious risks. Laboratories and their parent organizations also struggle with tightening budgets. From an IT perspective, these pain points include the ongoing costs to update and maintain IT infrastructures, performance and downtime issues, recruiting staff that has an understanding of the laboratory’s IT needs, and the increased liability and financial risk regarding handling of protected patient data (see Figure 5).
Many of Orchard’s LIS customers have reported concerns about the burden of managing their IT infrastructure, monitoring databases for optimal performance, preparing for environmental challenges and unexpected natural disasters, and developing security measures for ransomware attacks and other increased and evolving malicious risks. Laboratories and their parent organizations also struggle with tightening budgets. From an IT perspective, these pain points include the ongoing costs to update and maintain IT infrastructures, performance and downtime issues, recruiting staff that has an understanding of the laboratory’s IT needs, and the increased liability and financial risk regarding handling of protected patient data (see Figure 5).
Cloud-based laboratory solutions can be a highly effective method for expertly managing data, resources, and workflows. With vast flexibility for configuration, these models provide end users with built-in data integrity and security measures to keep data safe and help meet regulatory requirements. Moreover, cloud-based architecture provides a scalable solution to enable future business growth. The flexibility and scalability offered by cloud-based architecture permits rapid expansion of data management workflows without the need for substantial investment in internal IT resources.7
Key “HIT in the Cloud” Takeaways
The healthcare sector is under tremendous pressure to operate in real time and to provide easy access to data across multiple locations. Cloud services can help healthcare delivery organizations accomplish this transformation.
HIPAA-compliant cloud tools offer the healthcare industry many benefits, including cost savings, enhanced security and reliability, data sharing, custom applications, and expanded storage, giving organizations the ability to create a dynamic, future-ready infrastructure.
Cloud computing is expected to become the HIT infrastructure standard in the coming years, supporting continued development of EHRs and other clinical information systems, as well as healthcare analytics activities.
About Orchard’s Cloud Services
As our healthcare system continues to evolve, so do industry requirements for financing and IT deployment. Healthcare’s greater adoption of value-based care and its push toward interoperable systems requires that systems be more affordable and agile. The combined challenges that HIT faces today—monitoring systems to achieve optimal performance, minimizing and mitigating ever-growing security risks, and employing and retaining staff with technical expertise demand flexibility and affordability in information system deployment and ongoing support.
Flexible Financing & Cloud-based Deployment Options Available
In response to these changes, Orchard Software offers various financing and deployment options, such as a subscription model or a cloud-based deployment solution, where the system is hosted by Orchard in a Tier III data center. Benefits of a subscription model include elimination of large up-front capital expenditures, reduced labor and maintenance costs, and improvements in security measures.
Orchard Cloud Services offer a secure, reliable, and cost-effective hosting environment for your healthcare applications. Client systems are hosted in fully redundant, HIPAA-compliant data centers designed to protect and secure critical applications. Orchard hosting ensures that information systems are accessible and secure, allowing organizations to focus on their core mission—providing the highest quality care possible to the population they serve.

Benefits of Orchard’s Cloud-based Offerings
Healthcare-specific
- Includes cloud-native disaster recovery
- Understands unique security challenges of healthcare and PHI security
- Meets all HIPAA requirements
Reliability
- Redundancy throughout the production infrastructure
- Two TIER III-class data centers in separate locations with multiple power and cooling sources
Support, Backup, & Disaster Recovery
- 24/7 data availability backed by a service-level agreement
- Automatic installation of operating system, database, and application software updates
- Full weekly backup, with incremental backups nightly, and production database backup every 15 minutes
Compliance
- SSAE 18–compliant with annual third-party audit of all security/compliance controls
- HIPAA policy and methodology with third-party compliance audits conducted yearly
- HIPAA-designed technology architectures (e.g., encrypted data at rest and transport)
As always, Orchard is happy to listen to your individual situation and help you design a deployment and financing solution that works for your specific healthcare facility. For more information, please contact our sales team at (800) 856-1948 or sales@orchardsoft.com.
Reference List
- Global Market Insights. Healthcare cloud computing market to hit $55 billion by 2025: Global Market Insights Inc. https://www.prnewswire.com/news-releases/healthcare-cloud-computing-market-to-hit-55-billion-by-2025-global-market-insights-inc-300839513.html. Published April 29, 2019.
- Columbus L. 83% of healthcare organizations are using cloud-based apps today. Forbes. https://www.forbes.com/sites/louiscolumbus/2014/07/17/83-of-healthcare-organizations-are-using-cloud-based-apps-today/#aebb2093b729. Published July 17, 2014.
- MarketsandMarkets. Healthcare cloud computing market worth $51.9 billion by 2024. https://www.marketsandmarkets.com/PressReleases/cloud-computing-healthcare.asp. Published November 25, 2019.
- Douglas M. Top 6 benefits of cloud computing for healthcare. OutSystems. https://www.outsystems.com/blog/posts/cloud-computing-in-healthcare/. Published August 16, 2019.
- Kuo M, Kushniruk A, Borycki E. Cloud computing for health information management. Health-Management. 2013 (2). https://healthmanagement.org/c/healthmanagement/issuearticle/cloud-computing-for-health-information-management. Published 2013.
- Comstock J. Why healthcare data may be more secure with cloud computing. MobiHealth-News. https://www.mobihealthnews.com/content/why-healthcare-data-may-be-more-secure-cloud-computing. Published October 15, 2018.
- Evans K. Streamlining fertility treatment using clinical lab informatics solutions. MLO. https://www.mlo-online.com/management/article/21125861/streamlining-fertility-treatment-using-clinical-lab-informatics-solutions. Published February 20, 2020.


